Product Classification
Why need product classification?
- Not all products manufactured by insurance companies are insurance contracts
- Insurance contracts are those that contain significant insurance risk
How products are classified?
For valuation purposes, insurance contracts can be further classified into:
- Ordinary Life – Participating
- Ordinary Life – Non-Participating
- Personal Accident
- Unit-linked (Contracts with an explicit account balance)
- Universal life (Contracts with an explicit account balance)
- Group business (e.g. Group medical, Group life)
- Etc.
Valuation Methodology (Insurance Contracts – OL regular-pay)
Insurance Contract Liability/ Intangible Asset
- Benefit reserve (insurance contract liability)
- Maintenance expense reserve (insurance contract liability)
- Unearned profit premium (insurance contract liability)
- Deferred acquisition cost (intangible asset)
Valuation methodology
- Net Level Premium valuation
Selection of assumptions
- Best estimate PLUS Provisions for Adverse Deviation (PAD) on claims or interest rate, depending on the product types
Cohort assumption
- Assumptions are locked-in by cohort
Profit carrier
- Earned Premium
Unearned Profit Premium
- Unearned Profit Premium is setup to reflect the services provided throughout the coverage period (usually assumed to be uniform throughout the year)
- Profit premium would then be deferred and recognized in proportion to earned premium
Valuation Methodology (Insurance Contracts – OL Limited-Pay)
Valuation methodology
- Net Level Premium valuation
Selection of assumptions
- Best estimate PLUS Provisions for Adverse Deviation (PAD) on claims or interest rate, depending on the product types
Cohort assumption
- Assumptions are locked-in by cohort
Profit carrier
- Amount of insurance in force (mainly Sum Assured/ Net amount at risk effective from 2013NB cohort)
Insurance Contract Liability/ Intangible Asset
- Benefit Reserve
- Maintenance Expense Reserve
- Deferred Profit Liability (DPL)
- Deferred Acquisition Cost (Asset)
Contracts with an explicit account balance (e.g. universal life-type and investment-linked contracts)
Product Design
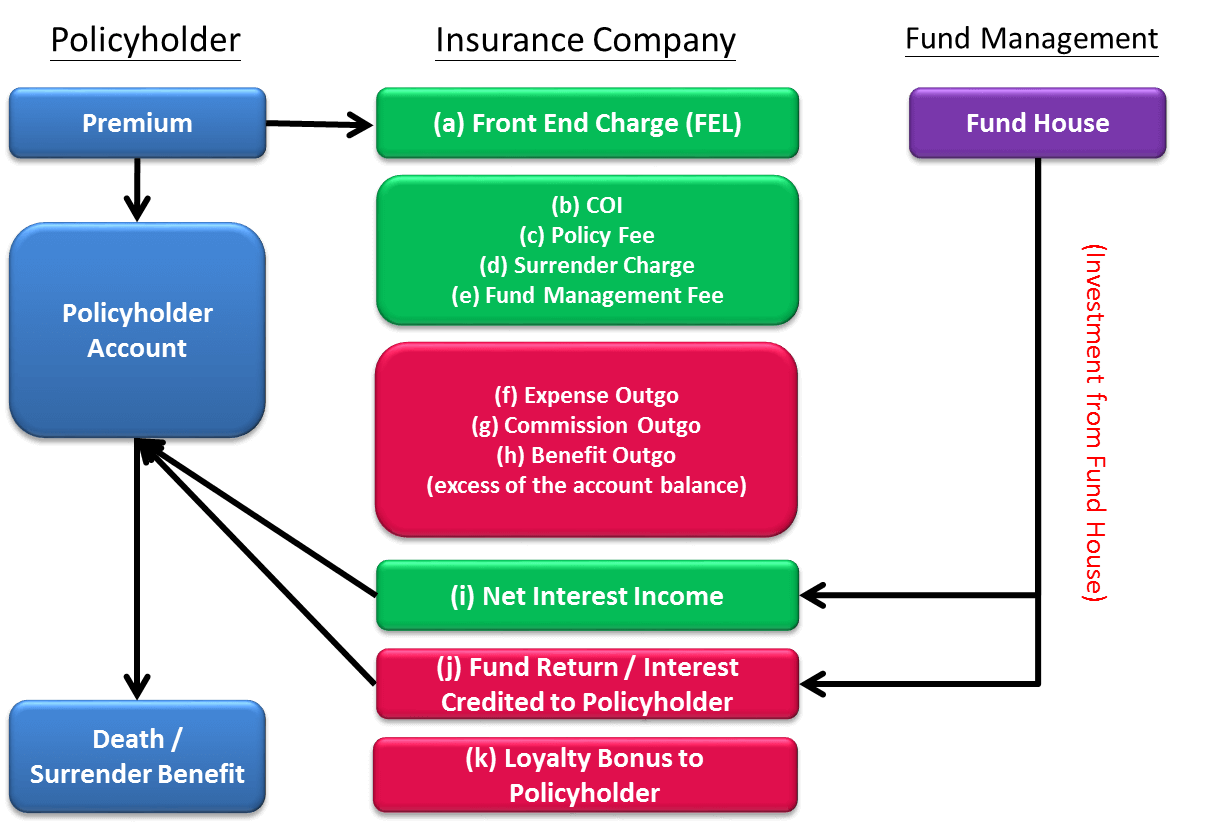
Accounting model & assumption
Accounting model
- Deposit accounting
Premiums are not reported as revenue to the company; fee income is revenue
- COI charges
- Surrender charges
- Expense charges
- Front-end loads in excess of ultimate loads: Deferred and amortized into income over the life of the contract in proportion to EGPs
If Benefits paid > Account Balance -> Costs to the company
Assumption
- Best Estimate (NO PAD!!)
- Unlocking
Discount rate for reserve of universal life contracts
Discount rate can be either:
- credited rate at inception
- current credited rate
AIA has adopted credited rate at inception as the discount rate.
Discount rate for reserve of unit-linked contracts
Discount rate is the fund growth rate net of fund management fee.
Profit Carrier
Estimated Gross Profit (EGP)
Insurance contract Liability/ Intangible Asset
- Accounting value
- Deferrable acquisition cost (DAC)
- Unearned revenue liability (URL)
- Sales inducement asset (SIA)
- Sales inducement liability (SIL)
- Additional insurance liability (AIL)
- Unearned COI
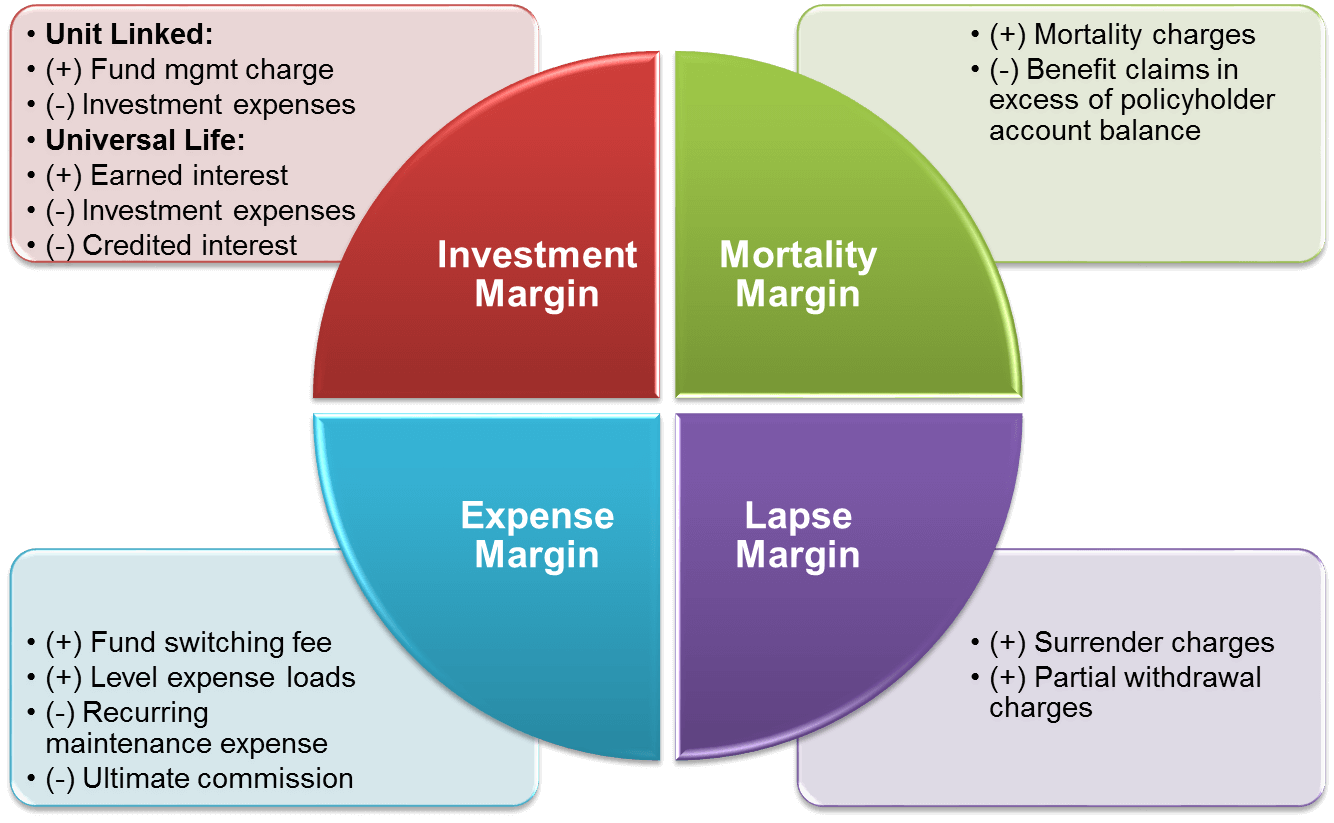
Source of Profit
- DAC/ URL Amortization
- Actual Gross Profit (AGP)
- Investment Margin
- Unit Linked:
- (+) Fund management charge
- (-) Investment expenses
- Universal Life:
- (+) Earned interest
- (-) Investment expenses
- (-) Credited interest
- Mortality Margin
- (+) Mortality charges
- (-) Benefit claims in excess of policyholder account balance
- Expense Margin
- (+) Fund switching fee
- (+) Level expense loads
- (-) Recurring maintenance expense
- (-) Ultimate commission
- Lapse Margin
- (+) Surrender charges
- (+) Partial withdrawal charges
- Non-AGP Items
- UDR Profit
- Overhead
- FY Non-Deferrable Expenses
- Non-Deferrable Variables
- Reinsurance gain/ loss
- Unit Linked:
- Investment Margin
IFRS Expense Classification
- Deferrable acquisition expense
- Non-Deferrable acquisition expense
- Direct maintenance expense
- Overhead
- Investment expense
Deferrable acquisition expense
- The costs of acquiring new and renewal business, including commissions, underwriting and other policy issue expenses, which vary with and are primarily related to the production of new business are deferred, provided that they are recoverable from future margins expected to be earned on inception of the contract.
- For commission & override, not the whole amount is deferrable, only the amount in excess of ultimate could be deferred
- The ultimate commission will be included in EGP.
Examples
Agent commission & Leader override (excess of ultimate), certain underwriting and policy issue expenses, and medical and inspection fees.
Non-Deferrable Acquisition Expenses
- Acquisition cost that do not vary with, or primarily relate to the securing of new policies. E.g. Market research, dividend determination for a new product
- Expense as incurred, directly hit P/L
Direct Maintenance Expenses
- Cost associated with maintaining records of the contract, policy servicing and termination. It includes ultimate commission. E.g. claims handling expense, premium collection payment
- Included in EGP
Overhead
- Expenses that not are categorized above
- do not vary with the amount of business in force and which are unrelated to the acquisition of new business. E.g. expense for producing statistics
- Expense as incurred, directly hit P/L
Investment Expenses
- Expense associated with investment activities. E.g. Investment personnel salary
IFRS Reserve and DAC calculation
Account Value Liability
Accrued Account Balance
- (+) Deposits net of withdrawals
- (+) Amounts credited pursuant to the contract
- (-) Fees and charges assessed
- (+) Additional interest (e.g. bonus)
- (+) Other adjustments
No reduction for anticipated surrender charges or similar fees
Deferred Acquisition Cost (DAC) Balance
Deferrable expenses:
- expenses which vary with and primarily relate to the acquisition of new business
- are amortized with interest over the life of the contract in proportion to EGP
Amortization rate is the % of future EGP required to provide for deferred policy acquisition costs
k−DAC = PV of Deferrable Expenses at t=0 / PV of EGP at t=0
